Telstrat is a different recording solution implemented in multiple Contact Centers. In the following entries we will verify the integration and analyze the requirements and configurations in a lab environment.
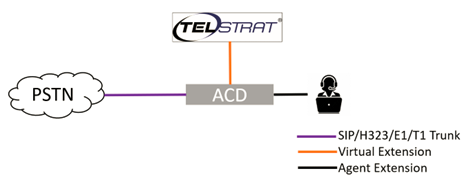
Integration of Telstrat is accomplished using a method called active call recording. This means that instead of using a passive way of getting the audio, active call recording (Telstrat) “jumps” into the call to get a copy, this is performed in two steps:
- Registering virtual stations in the PBX/ACD
- Doing a “Service Observing/Conferencing” which creates a copy of the audio
This is a simplified diagram showing how Telstrat works:
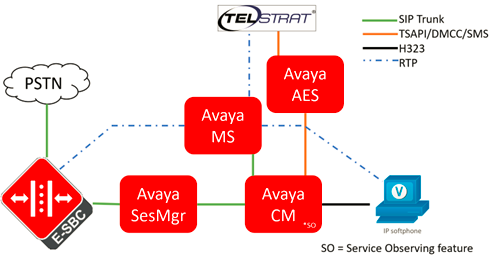
Now let’s move on to the integration that we will be working in this lab, applying a few changes in the previous diagram to reflect the current devices we will be working with:
- ACD will be replaced by:
- Avaya Communication Manager work as the PBX/ACD for agents working with softphones
- An additional feature will be required in the Communication Manager to have the “Service Observing” enabled for the virtual extensions used by Telstrat to “jump” into the ACD calls
- Avaya Media Server which serves as the processor for audio/RTP
- Avaya Session Manager process the signaling connection between the Oracle SBC and the Avaya CM
- Avaya Application Enablement Services provide the integration of Avaya world to Telstrat with:
- Virtual extension control and events using TSAPI
- RTP control on virtual extensions using DMCC (DMCC always work in conjunction with TSAPI)
In the next entries we will work in a few specific required configurations to have Telstrat recording integrated in this lab environment. As many of the tasks have been already worked in previous entries, they will be only mentioned to avoid extending the entries unnecessarily.
